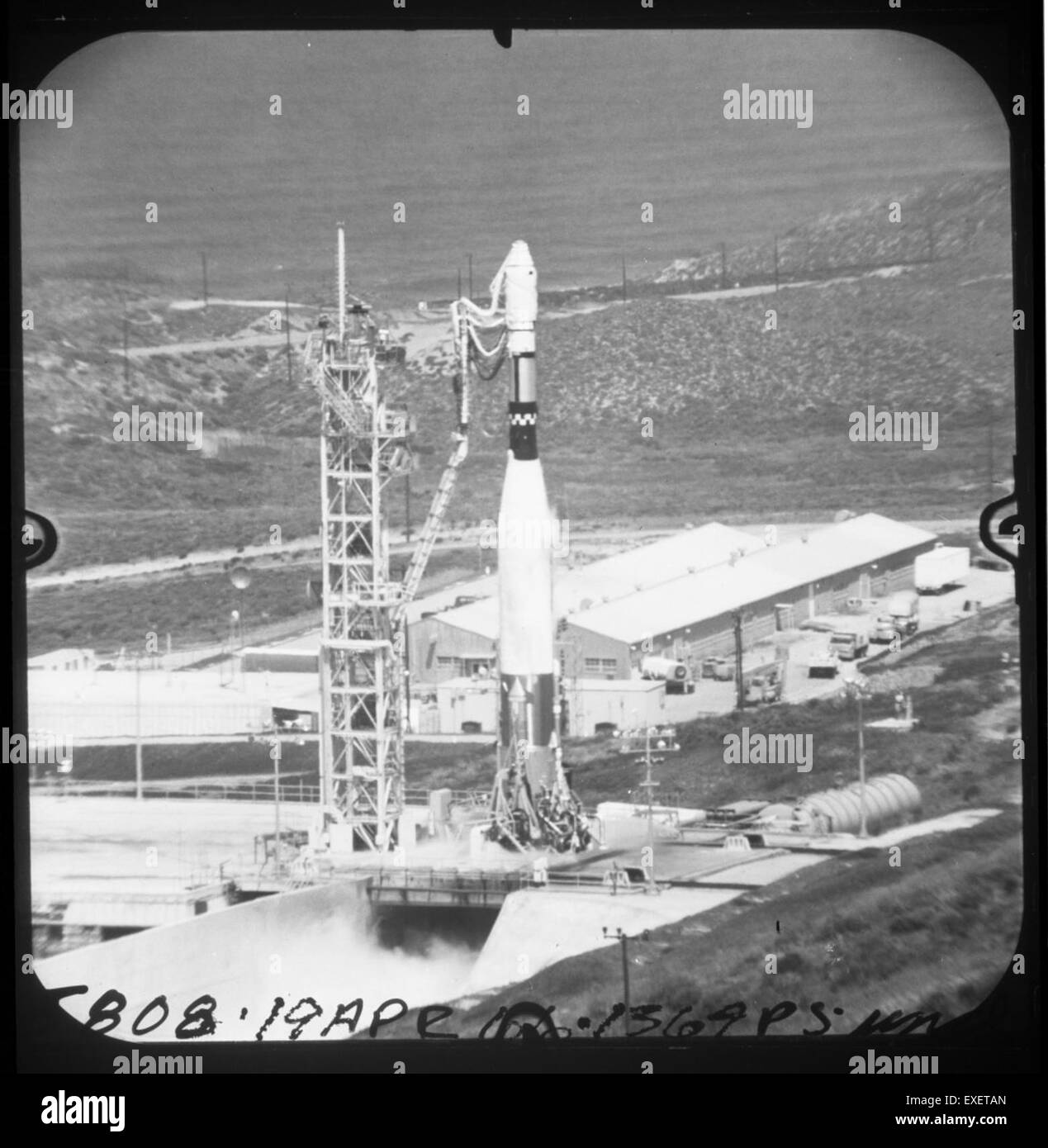


What is not commonly known by today’s space enthusiasts is that the current version of this booster can trace its origins back in 1957 when the first Atlas flew.
Elektron 2 | Ranger 6 | OPS 3444 | Zond 3MV-1 No.2 | Kosmos 25 | OPS 2423 | OPS 3722 | OPS 3435 | Kosmos 26 | BE-A | Luna E-6 No.6 | OPS 3467 | Kosmos 27 | Ariel 2 | Zond 1 | Kosmos 28 | Gemini 1 | Polyot 2 | Luna E-6 No.5 | Transit 5BN-3.OPS 3367B | Relay 2 | Echo 2 | Jupiter Nosecone | Elektron 1.Space Flight Operations Plan Mariner Mars '64 (PDF).Mariner 3 Mission Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration.Jet Propulsion Laboratory/ California Institute of Technology, NASA. 33-229, To Mars: The Odyssey of Mariner IV (PDF) (Report). Mariner 3, dead and still ensnared in its faulty launch shroud, in a large orbit around the sun. "Spaceflight Operations Plan Mariner Mars '64" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on Octo. ^ "Mariner Mars 1964 Mechanical Configuration" (PDF).Three weeks later, on November 28, 1964, Mariner 4 was launched successfully on a 7½-month voyage to Mars. Even if the shroud could be removed, the mission probably would have failed anyway since the low velocity meant that Mariner 3 would miss Mars by several million miles. Eight hours after launch, the batteries in the probe died and the mission was officially terminated. The ground controllers next considered firing Mariner 3's midcourse correction engine to blow off the shroud, but they ran out of time. A command was sent to manually jettison the payload shroud, but nothing happened. Telemetry data suggested a separation failure of either the Agena or the payload fairing, but a below-normal velocity appeared to indicate that the fairing had not separated properly. Unsure of the exact problem, ground controllers issued a command to turn off the rate gyros to conserve power while they worked to figure out what had happened. One hour after launch, the first telemetry transmissions from Mariner 3 were received, indicating that the scientific instruments were functioning correctly but there was no indication of any solar panel operation. After an uneventful boost phase, the Agena completed its burn to place the probe on a trajectory towards Mars. Mariner 3 was launched at 2:22 PM EST on November 5, 1964, from Cape Kennedy Air Force Station Launch Complex 13. Atlas vehicle 289D was erected on the pad on August 17, with the backup Mariner probe and booster (Atlas 288D) erected on LC-12 on September 28. Of the two Atlas-Agena pads at Cape Canaveral, LC-13 became available first following the launch of an Air Force Vela satellite in July 1964. Mariner 3 also utilized a new, larger fiberglass payload fairing. Because of the greater mass, the new Agena D stage would be used instead of the Agena B.
#Atlas agena payload tv#
Mariner 2 had been a modified Ranger lunar probe, however Mariner 3 used a new, larger bus with four solar panels, a TV camera, and additional instrumentation. It was the third of ten spacecraft within the Mariner program. Īlthough the launch was initially successful, there was a separation issue and Mariner 3 stopped responding when its batteries ran out of power.

Mariner 3 (together with Mariner 4 known as Mariner-Mars 1964) was one of two identical deep-space probes designed and built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) for NASA's Mariner-Mars 1964 project that were intended to conduct close-up (flyby) scientific observations of the planet Mars and transmit information on interplanetary space and the space surrounding Mars, televised images of the Martian surface and radio occultation data of spacecraft signals as affected by the Martian atmosphere back to Earth.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
